Chiglintseva A.S., Shagapov V.Sh.
The theory of injection of a hydrate-forming gas into a snow massif saturated with the same gas.
Multiphase Systems. 13 (2018) 4. 92–98.
The theory of injection of a hydrate-forming gas into a
snow massif saturated with the same gas
Chiglintseva A.S.∗,∗∗, Shagapov V.Sh.∗,∗∗∗
∗Mavlutov Institute of Mechanics, UFRC RAS, Ufa
∗∗Ufa State Petroleum Technological University, Ufa
∗∗∗Institute of Mechanics and Engineering, Kazan Scientific Center of the RAS, Kazan
Abstract
The mathematical model of the process of gas hydrate
formation during gas injection into a snow massif, saturated with the same gas, is constructed.
In axisymmetric formulation, analytical solutions are obtained for the distribution of
temperature fields, pressures and phase saturations. It is shown that the appearance of
various characteristic zones in a snow massif depends on the initial state of the gas–snow
system, determined by temperature and pressure, and the mass flow rate of the injected gas.
It has been established that an increase in the intensity of gas injection (gas flow rate)
leads to an increase in both the length of the bulk zone of hydrate formation and the increase
in the fraction of hydrate at the boundary separating the near and intermediate zones.
Keywordsgas hydrate,
snow massif,
filtration,
self-similar solutions
Article outline
In order to create a technology for the storage and
utilization of greenhouse, radioactive, industrial and other gases in a gas hydrate state,
the mathematical model of the process of injection of hydrate-forming gas into a snow massif,
in the initial state saturated with the same gas was developed. Self-similar solutions
describing the fields of temperatures, pressures, and saturation of snow, water, hydrate,
and gas in the massif for the axisymmetric problem are obtained. It is shown that depending
on the intensity of gas injection, determined by the mass flow value, different characteristic
zones can occur in the filtration zone. However, at sufficiently large gas flow rates,
a regime may arise in which the temperature in the massif may be higher than the melting
temperature of the ice, which will lead to the appearance of the water phase. To obtain a
physically consistent solution, the mathematical model was constructed with three moving
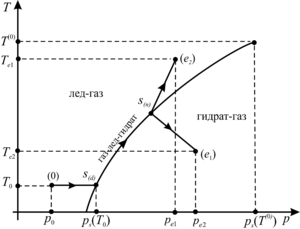
frontal boundaries. If gas injection occurs under thermobaric conditions corresponding
to hydrate formation, in this case, the near region adjacent to the well will be saturated
with gas and hydrate phases, and in the case of the absence of hydrate formation, with snow
and gas. Next, an intermediate region is formed in which gas and snow transform into
the hydrate, and a distant region filled with the initial phases of gas and snow.
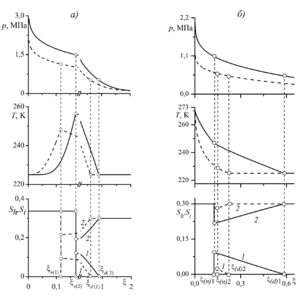
According to numerical calculations, the increase in the mass flow rate of gas leads
to an increase in the length of the hydrate formation zone and hydrate saturation
at the border separating the near and intermediate regions. The results obtained
in solving such problems represent some initial stage of gas hydrate formation in massif
and layers of finite length, and can be used to test the selected numerical algorithms.
References
- Истомин В.А., Якушев В.С. Газовые гидраты в природных
условиях. М.: Недра, 1992, 236 c.
- Бондарев Э.А., Рожин И.И., Попов В.В., Аргунова К.К. Оценка возможности
подземного хранения гидратов природного газа в зоне многолетней мерзлоты //
Криосфера Земли. 2015. Т. XIX, №4. С. 64–74.
(http://www.izdatgeo.ru/pdf/krio/2015-4/64.pdf)
- Nakai S. Development of Natural Gas Hydrate (NGH) Supply Chain //
Proceedings, 25th World Gas Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 4-8 June. 2012. Pp. 3040–3050.
- Shagapov V.Sh., Khasanov M.K., Musakaev N.G. Formation of a gas hydrate due to injection
of a cold gas into a porous reservoir partly saturated by water // Journal of Applied
Mechanics and Technical Physics. 2008. V. 49, No. 3. Pp. 462–472.
(DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer. 2015.01.105)
- Шагапов В.Ш., Чиглинцева А.С. О нагнетании гидратообразующего газа в снежный массив,
насыщенный тем же газом, при переходе через точку плавления льда // Теплофизика и
аэромеханика. 2018. Т. 25, №1. С. 89–104.
(DOI: 10.1134/S0869864318010080)
- Чиглинцева А.С. Автомодельное решение задачи образования гидрата в снежном массиве //
Вычислительная механика сплошных сред. 2017. Т. 10, №2. С. 212–224.
(DOI: 10.7242/1999-6691/2017.10.2.18)
- Чиглинцева А.С. Автомодельная задача о нагнетании гидратообразующего холодного газа в
снежный массив, насыщенный тем же газом // Неравновесные процессы в сплошных средах:
материалы междунар. симп.: в 2 т. / Перм. гос. нац. исслед. ун-т. Пермь. 2017. Т. 2. С. 236–238.
- Чиглинцева А.С., Шагапов В.Ш. О нагнетании гидратообразующего газа в пласт снега,
насыщенный тем же газом // Труды Института механики им. Р.Р. Мавлютова УНЦ РАН. 2017. Т. 12,
№2. С. 219–226.
(DOI: 10.21662/uim2017.2.033)
- Хасанов М.К. Исследование режимов образования газогидратов в пористой среде, частично
насыщенной льдом // Теплофизика и аэромеханика. 2015. Т. 22, №2. С. 255–266.
(DOI: 10.1134/S0869864315020109)
- Шагапов В.Ш., Мусакаев Н.Г. Динамика образования и разложения гидратов в системах добычи,
транспортировки и хранения газа. М.: Наука, 2016. 238 с.
- Нигматулин Р.И. Динамика многофазных сред: в 2 ч. М.: Наука, 1987.
- Шагапов В.Ш., Чиглинцева А.С., Русинов А.А. Теоретическое моделирование процесса
извлечения газа из пористого газогидратного резервуара частично насыщенного газом с
учетом теплового взаимодействия с окружающими породами // Теоретические основы химической
технологии. 2016. Т. 50, №4. С. 452–462.
(DOI: 10.7868/S004035711604014X)
- Шагапов В.Ш., Чиглинцева А.С., Русинов А.А. Математическое моделирование процесса
образования гидрата в пласте насыщенного снегом при нагнетании холодного газа //
Вычислительная механика сплошных сред. 2016. Т. 9, №2. С. 173–181.
(DOI: 10.7242/1999-6691/2016.9.2.15)
- Шагапов В.Ш., Чиглинцева А.С., Белова С.В. К теории процесса образования газогидрата
в замкнутом теплоизолированном объеме, опрессованном метаном // Инженерно-физический
журнал. 2017. Т. 90, No. 5. С. 1208–1222.
(DOI: 10.1007/s10891-017-1669-8)
- Шагапов В.Ш., Галимзянов М.Н., Запивахина М.Н. Моделирование процесса образования льда
при инжекции воды в пористую среду, насыщенную льдом и газом // Вестник
Башкирского университета. 2013. Т. 18, №1. С. 22–26.
(https://elibrary.ru/download/elibrary_18956893_55543496.pdf)
- Шагапов В.Ш., Галимзянов М.Н., Запивахина М.Н. Моделирование процесса образования льда
при нагнетании воды в сухую пористую среду // Известия Уфимского научного
центра РАН. 2016. №4. С. 14–18.
(https://elibrary.ru/download/elibrary_27521020_53771951.pdf)