Nasibullayev I.Sh., Nasibullaeva E.Sh., Darintsev O.V.
Study of fluid flow through a channel deformed by piezoelement.
Multiphase Systems. 13 (2018) 3. 1–10.
Study of fluid flow through a channel deformed by piezoelement
Nasibullayev I.Sh., Nasibullaeva E.Sh., Darintsev O.V.
Mavlutov Institute of Mechanics, UFRC RAS, Ufa
Abstract
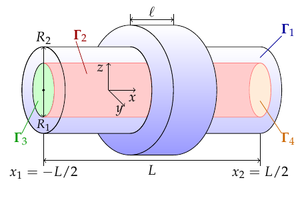
The flow of a liquid through a tube deformed by
a piezoelectric cell under a harmonic law is studied in this paper. Linear deformations
are compared for the Dirichlet and Neumann boundary conditions on the contact surface
of the tube and piezoelectric element. The flow of fluid through a deformed channel
for two flow regimes is investigated: in a tube with one closed end due to deformation
of the tube; for a tube with two open ends due to deformation of the tube and
the differential pressure applied to the channel. The flow rate of the liquid is calculated
as a function of the frequency of the deformations, the pressure drop and the physical
parameters of the liquid.
Keywordshydrodynamics,
hydrodynamic resistance,
piezoelement,
linear elasticity,
finite element method
Article outline
Purpose: the development of a three-dimensional
computer model of fluid flow in a channel with a hydrodynamic resistance, where the form of
the hydro resistivity varies according to the periodic law and is determined by the
deformation of the tube by the piezoelectric element.
Methodology: the Lame equations were solved by the finite element method in the FreeFem ++
package. The equations of hydrodynamics were discretized in time according to the Euler
scheme and solved by the finite element method in the FreeFem ++ package; The solution of the
nonlinear problem was found by Picard iterations.
The findings of research:
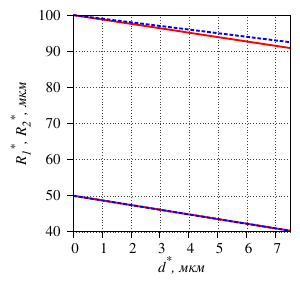
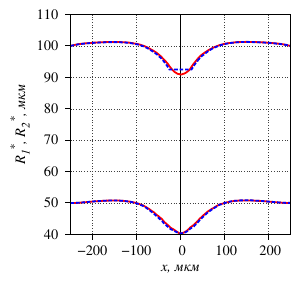
- the interchangeability of the Neumann and Dirichlet boundary conditions is shown: by
selecting the piezoelectric element pressure on the outer part of the tube, one can obtain the
same deformation of the inner part of the tube as when setting the displacement of the contact
surface inwards by a define value (the dependence is linear);
- studied two fluid flow regime in the deformed tube: the tube inlet is closed, the
flow induced tube deformation; both ends are open, the flow is induced both by the
deformation of the tube and by the differential pressure applied to the layer. The first regime
allows one to test the computer model, and the second regime allows one to offer a liquid
dosing mechanism controlled by two parameters: the piezoelement compression rate and the
differential pressure;
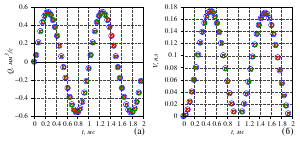
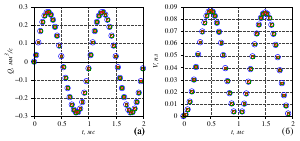
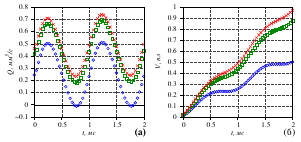
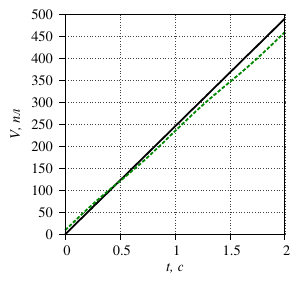
- it is found that the fluid flow rate depends on the compression frequency of the
piezoelectric element and, if there is no pressure drop, does not depend on the physical
parameters of the fluid. This theoretically makes it possible to implement a hydraulic
microdrive with a linear ”mechanical“ (consumable) characteristic;
- under the influence of the pressure drop, a constant component inversely proportional to
the viscosity of the liquid is added to the periodic component of the fluid flow;
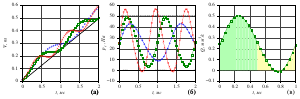
- it is shown that one can obtain a flow regime corresponding to the droplet extrusion
by selecting parameters (frequency, pressure drop). The volume of the droplet squeezed out
during the period decreases with increasing frequency.
Originality/value: The proposed computer model describing the fluid behavior in
microchannels using piezoelectric drives is the first step in
developing a theoretical basis for creating microdrives and executive micromechanisms.
References
- Bruus H. Theoretical microfluidics. Lecture notes third edition.
MIC Department of Micro and Nanotechnology Technical University of Denmark. 2006.
URL: http://homes.nano.aau.dk/lg/Lab-on-Chip2008_files/HenrikBruus_Microfluidics%20lectures.pdf
(дата обращения: 10.04.2018).
- Stroock A.D., Dertinger S.K.W., Ajdari A. et al. Chaotic Mixer for
Microchannels // Science. 2002; Vol. 295(5555). Pp. 647–651.
(DOI: 10.1126/science.1066238)
- Насибуллаев И.Ш. Разработка компьютерной модели основного элемента агрегата дозирования топлива //
Вычислительные технологии. 2016. Т. 21, № 2. С. 26–41.
(http://www.ict.nsc.ru/jct/annotation/1724)
- Насибуллаев И.Ш., Насибуллаева Э.Ш., Денисова Е.В. Динамика течения жидкости
в технических системах с жиклерами // Известия Уфимского научного центра РАН. № 4. 2015. С. 20–25.
(http://sciencerb.ru/vyp/4_2015/20-25.pdf)
- Насибуллаев И.Ш., Насибуллаева Э.Ш. Влияние температуры на динамику течения жидкости
в технических системах с жиклерами // Труды Института механики им. Р.Р. Мавлютова
Уфимского научного центра РАН. 2016. Т. 11, № 1. С. 1–9.
(DOI: 10.21662/uim2016.1.001)
- Насибуллаев И.Ш., Насибуллаева Э.Ш. Течение жидкости через систему связанных элементов
технического устройства типа труба–гидросопротивление–труба // Труды Института
механики им. Р.Р. Мавлютова Уфимского научного центра РАН. 2016. Т. 11, № 2. С. 141–149.
(DOI: 10.21662/uim2016.2.021)
- Насибуллаев И.Ш., Насибуллаева Э.Ш. Течение жидкости через гидросопротивление с
динамически изменяемой геометрией // Труды Института механики им. Р.Р. Мавлютова
Уфимского научного центра РАН. 2017. Т. 12, № 1. С. 59–66.
(DOI: 10.21662/uim2017.1.009)
- Ландау Л., Лифшиц Е.М. Теоретическая физика. Т. 7. Теория упругости. М.: Наука, 1987. 248 с.
- Hecht, F. New development in FreeFem++ // J. Numer. Math. 20 (2012), no. 3–4, 251-–265. 65Y15.
(DOI: 10.1515/jnum-2012-0013)
- Ландау Л., Лифшиц Е.М. Теоретическая физика. Т. 6. Гидродинамика. М.: Наука, 1988. 736 с.
- Белоусов К.И., Евстрапов А.А., Кухтевич И.В., Посмитная Я.С.
Основы нанотехнологий. Часть 1. Микро- и нанотехнологии для биологических и медицинских
исследований. Часть 2. Капельная микрофлюидика: Учеб. пособие. СПб: Университет ИТМО, 2015. 56 с.
(http://books.ifmo.ru/file/pdf/1839.pdf)